Language and Culture/UI Culture or Internationalization in MVC
Setting
up Language and UI Culture in efficient way is very important. Also, there are
many ways to achieve this today but the best way is always easy to achieve,
clean, documented. I can see many posts online about this but they not much
useful and end to end discussed, you end up with huge code.
In
this post we will discuss a best possible way to achieve this. Using the suggested
approach here you can localize-culture Model Metadata and Validations which
includes Display, Required, StringLength etc. I’m going to select an empty
project template for MVC, you will find source code repository link at the end
of this post.
Let’s
break this post into sections:
1. Creating
Model Metadata and Validations Localizations
2. Attaching
Resource Files & Language and Culture Selector
1. Creating Model Metadata and Validations
Localizations
Let’s
assume we have a simple model class:
public class Friend
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Mobile { get; set; }
public string Address { get; set; }
}
Now, to
make it little useful and to start validation we will change above class to
something like this:
public class Friend
{
public int Id { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Full
Name")]
[Required]
[StringLength(50)]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Contact
Number")]
[Required]
[StringLength(15)]
public string Mobile { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Full
Address")]
[Required]
[StringLength(150)]
public string Address { get; set; }
}
Now,
we want localization using data annotations, then above class will become:
public class Friend
{
public int Id { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Full
Name", ResourceType = typeof(ClassName.Resources))]
[Required(ErrorMessageResourceType = typeof(ClassName.Resources), ErrorMessageResourceName = "Friend_Name_Required")]
[StringLength(50, ErrorMessageResourceType = typeof(ClassName.Resources),
ErrorMessageResourceName = "Friend_Name_StringLength")]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Contact
Number", ResourceType = typeof(ClassName.Resources))]
[Required(ErrorMessageResourceType = typeof(ClassName.Resources), ErrorMessageResourceName = "Friend_Mobile_Required")]
[StringLength(15, ErrorMessageResourceType = typeof(ClassName.Resources),
ErrorMessageResourceName = "Friend_Mobile_StringLength")]
public string Mobile { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Full
Address", ResourceType = typeof(ClassName.Resources))]
[Required(ErrorMessageResourceType = typeof(ClassName.Resources), ErrorMessageResourceName = "Friend_Address_Required")]
[StringLength(150, ErrorMessageResourceType = typeof(ClassName.Resources),
ErrorMessageResourceName = "Friend_Address_StringLength")]
public string Address { get; set; }
}
Notice
how our super clean model started becoming super clutter model and this will
keep growing.
So
what we can do to get rid of all that dirts. MVC is has power and we need some
sort of conventions by which I should be able to look up error messages in
resource files as well as property labels without having to specify all that
information. In fact, by convention I shouldn't even need to use the Display
annotations.
So,
we will stick with simple and clean class which is:
public class Friend
{
public int Id { get; set; }
[Required]
[StringLength(50)]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Required]
[StringLength(15)]
public string Mobile { get; set; }
[Required]
[StringLength(150)]
public string Address { get; set; }
}
The
starting point is configuring model metadata providers in Application_Start in
Global.asax file.
ModelMetadataProviders.Current = new ConventionalModelMetadataProvider(false, typeof(Resource));
Here I
set false for required convention attribute for model class. This way I do not
need to specify any attribute with class. The parameter Resource will be
developed in #2, so let’s keep it showing error. I will store
ConventionalModelMetadataProvider class in a new folder ‘ModelMetadataExtension’.
Here is the code which takes the call.
public class ConventionalModelMetadataProvider : DataAnnotationsModelMetadataProvider
{
public ConventionalModelMetadataProvider(bool requireConventionAttribute)
: this(requireConventionAttribute, null)
{
}
// More
methods here, check GitHub
}
Here
ConventionalModelMetadataProvider class implements DataAnnotationModelMetadataProvider
which is default model metadata provider of MVC. Check GitHub to see rest codes
in this class file.
Now, ConventionalModelMetadataProvider
class requires some attributes to be defined which I have defined inside ModelMetadataExtension
> Extensions folder, check GitHub for that.
At this
point of time if you build project you should see just one error which is Resorce,
here.
ModelMetadataProviders.Current = new ConventionalModelMetadataProvider(false, typeof(Resource));
Now,
let’s switch to next section where we will create our resource files.
2. Attaching Resource Files & Language and
Culture Selector
As I
said, there many ways to use resource files. We can hardcode it somewhere or
relay on the user’s machine settings. But this is not preferred way, what preferred
way is by using route parameters that sets the culture and language, like:
Whenever
user visits http://www.example.com/en-US/etc
this should use English version resource file and whenever user visits http://www.example.com/hi-IN/etc
this should use Hindi version resource file.
The
starting point here is creating resource files one for English and another for
Hindi. I am going to add resource files inside a new special folder ‘App_GlobalResources’.
Now add two resource files Resource.resx (default resource file) and Resource.hi-IN.resx.
Once we have resource file this code should resolve and project should build
without any error.
ModelMetadataProviders.Current = new ConventionalModelMetadataProvider(false, typeof(Resource));
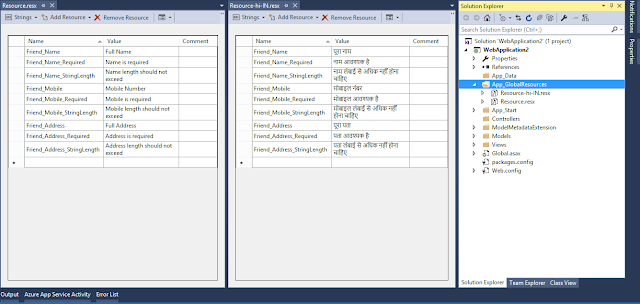
Open
resource files in resource editor and type localized messages as given below (click
to enlarge):
Notice
the name of the property in resource file, this should always follow convention
as listed below:
Display
Annotation: modelClassName_classProperty
Required
Annotation: modelClassName_classProperty_Required
StringLength
Annotation: modelClassName_classProperty_StringLength
To translate
English message in Hindi I took goggle translator help from here.
Now
three more things to do, i) add a new route ii) add new action filter attribute
to check route language-culture iii) use attribute with controller class
i) Add a new route
For
this add a new top level route in the route list, here is the code:
routes.MapRoute(
"DefaultLocalized",
"{language}-{culture}/{controller}/{action}/{id}",
new
{
controller = "Home",
action = "Index",
id = UrlParameter.Optional,
language = "en",
culture = "US"
});
ii) Add new action filter attribute
I
will add new action filter class by name ‘InternationalizationAttribute’ inside
ModelMetadataExtension folder again, here is the code:
public class InternationalizationAttribute : ActionFilterAttribute
{
public override void OnActionExecuting(ActionExecutingContext filterContext)
{
string language = (string)filterContext.RouteData.Values["language"] ?? "en";
string culture = (string)filterContext.RouteData.Values["culture"] ?? "US";
Thread.CurrentThread.CurrentCulture = CultureInfo.GetCultureInfo(string.Format("{0}-{1}",
language, culture));
Thread.CurrentThread.CurrentUICulture = CultureInfo.GetCultureInfo(string.Format("{0}-{1}",
language, culture));
}
}
Notice
I’m setting up English en-US as default which maybe anything other language in
your case. Ideally, this should be used when supporting more than two languages
because default should be always English which should not be in above code.
iii) Use attribute with controller
I’m
using action filter ‘Internationalization’ which needs to be applied as globally
or controller by controller. Let’s apply on controller as given below:
[Internationalization]
public class FriendsController : Controller
{
private DemoFriendContext db = new DemoFriendContext();
//
Action methods lists
}
Now
let’s run the application you will see everything working correctly. The
display annotation, required annotation, string length everything. Here is in action screenshot (click to enlarge):
Source
Code: GitHub
Hope
this helps.


How to localize from database instead of resource file in MVC.........any idea
ReplyDelete