Model First Approach in Entity Framework
Introduction
Read
my previous two posts ‘Code First Approach in Entity Framework’ &
‘Database First Approach in Entity Framework’ for
EF basics. In this post I’m directly going to jump on Model First Demo Project.
Demo MVC Application
Create
a new ASP.NET MVC Project by New > Project > ASP.NET MVC 4 Web
Application > ‘Internet Application’ Template because this template contains
required js/css bundles and account setup. Even choosing ‘Internet Application’
as a template adds all required binaries for EF developments including
‘System.Data.Entity’.
Follow
the steps for further demo.
Step 1: Adding ‘ADO.NET
Entity Data Model’ File
For
this, right click on Models > Add > New Item and in the Data section
select ‘ADO.NET Entity Data Model’ and click on Add button. It will bring an
‘Entity Data Model Wizard’, in this window select ‘Empty model’, because we are
going to create ‘Model First’ demo and click on finish button. You will get a
‘Model1.edmx[Diagram1]’ file this is also known as ‘Entity Data Model Designer’
and here we will design our database tables and also create the relationships.
Step 2: Adding Entity
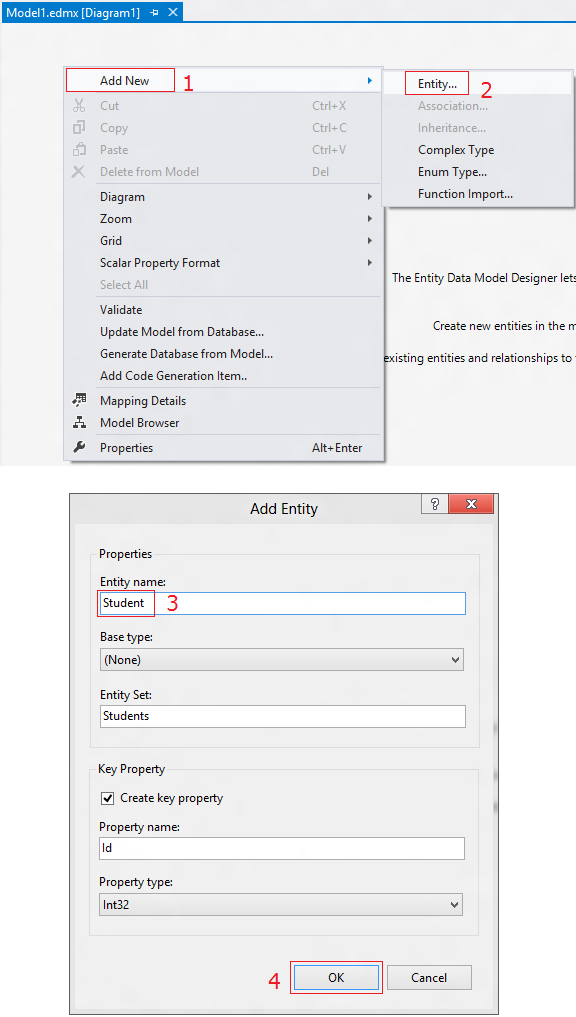
To
add Entity, right click on ‘Entity Data Model Designer’ surface and chose Add
New > Entity and it appeared windows type Entity name as ‘Student’ and click
on ok.
Step 3: Adding Properties
for ‘Student’
Now,
you got ‘Student’ mode, let’s add properties for this. There is two different
ways to add properties.
Right
click on ‘Student’ mode and navigate to Add New > Scalar Property.
OR
Select
‘Id’ in ‘Student’ mode and press enter key on keyboard, this will bring a new
property asking to enter name.
Step 4: Adding
Relationships
Now,
create following structure (two entities) by repeating step 2 and 3.
Now,
we got two different entities on the ‘Entity Data Model Designer’ surface. Here
we need a relationship between both entities like for each Student in ‘Student’
entity there will be many marks in ‘Mark’ entity. Means the concept is, we
don’t want/accept any mark in ‘Mark’ entity which has no relation to ‘Student’
entity.
Now,
for such structure we need to create relationship by adding ‘Association’.
Right click on designer surface and select Add New > Association.
Now,
you will get following window asking to arrange the relationship.
Don’t
make any changes, because VS done everything we want smartly. We just need to
understand options. As I said above, for every Student there will be many marks
in Mark entity. We also got an Association Name (it is just a name of this
relationship) and Navigation Property, let’s talk about this in depth.
Navigation
Property
Navigation
properties in the Entity Framework provide a way to navigate an association between
two entity types. A navigation property is defined by the NavigationProperty
Element (CSDL) in the conceptual model. Every object can have a navigation
property for every relationship in which it participates. Navigation properties
allow you to navigate and manage relationships in both directions, returning
either an EntityReference, if the multiplicity is either one or zero-or-one, or
an EntityCollection, if the multiplicity is many. You may also choose to have
one-way navigation, in which case you can delete the navigation property.
In
simple word, navigation property just shows that there is some relation it
maybe one to many, many to many, zero or one and displays the graphical line
between both entities.
Foreign
Key Property
You
will also notice a checkbox in above image. The main characteristic of Foreign
key association is a foreign key property exposed on a dependent entity. The
foreign key property must be always exposed when you wish not to accept any
entry who’s ‘StudentId’ is not available in ‘Student’ entity.
Note:
If you try to delete ‘Student’ table before deleting ‘Mark’ table, you will get
error message showing there is some dependencies.
Step 5: Configuring Model
Properties
Just
click on ‘Entity Data Model Designer’ surface and open the properties window.
In
above image, you can modify the marked properties if you wish or keep it
default.
Step 6: Generate Database
from above model
Now,
we have everything setup to create database from above structured model. For
this, right click on ‘Entity Data Model Designer’ surface and select ‘Generate
Database from Model’.
Now,
in the appeared window, you can go with the default connection, I’m going to
create a new connection.
And
click on next button, it will generate a sql query and this query will be
executed against above selected database. Now, click on finish to get sql file
containing all sql information’s like how to created db, what will be the name
of tables and what will be the relations etc.
You
can handover the above query information to db end person to generate the
database for your app. Let’s execute this query against above selected
connection for now by right clicking on query file.
After
executing the query file, you will notice a database with some tables that we
have designed above.
Step 7: Adding Controller
and Views
Let’s
build the solution here Build > Build Solution, this will bring classes (in
our case Model1.Designer.cs’) in Add Controller window.
Now,
time to add controllers and views for both entities. Let’s begin by adding
‘Student’ controller.
Right
click on Controller > Add > Controller and make following selection as given
in image.
If
you click on Add button above, will add required controller and its methods and
also different views.
We
need to add one more controller for ‘Mark’ entity, repeat above instructions
and you will get following files.
Step 8: Running
Application
Now
run apps and try to insert record in ‘Mark’ without inserting any record in ‘Student’,
you will be asked to select ‘Student’ here and still we don’t have any entry in
‘Student’. So, now we can see the impact of ‘Foreign Key’ here.
Let’s
go back and make an entry in ‘Student’ and then in ‘Mark’ and you will get the
list of Student here.
So,
that’s all about the ‘Model First’ approach in Entity Framework. Thanks.


















Comments
Post a Comment